Fri, Dec 13, 2024
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 4 (December 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(4): 1-12 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
HASSAN A. Investigation on Surface Hardness and Microstructure Evolution in AA 7075-T651 Multi-Layered Laminate Fabricated Through Friction Stir Additive Manufacturing. IJMSE 2023; 20 (4) :1-12
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3361-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3361-en.html
Abstract: (7916 Views)
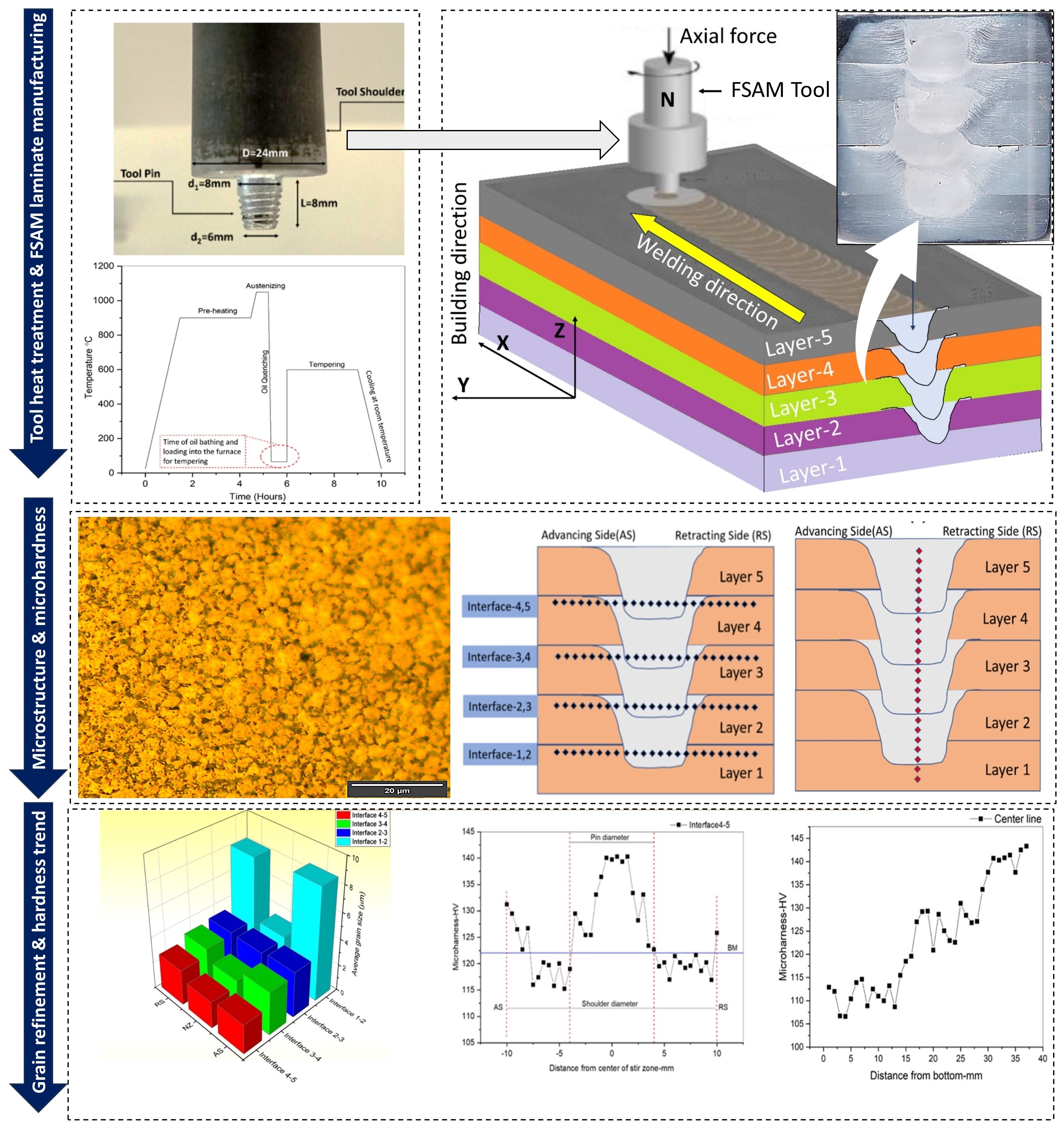
Friction stir additive manufacturing (FSAM) is a variant of sheet lamination additive manufacturing used to produce large, near-net-shaped 3D parts. Unlike traditional friction stir lap welding, FSAM introduces a new plate to one that is already joined, with the effective area limited to the nugget zone. The present study focuses on exploring the microstructure and microhardness around the nugget zone in a five-plate AA 7075-T651 laminate synthesized at 1000 rpm and 35 mm/min. Microhardness increased vertically in the weldment NZ, reaching 143 HV in the top layer with 2.0 μm fine equiaxed grains. The grains on the advancing and retreating sides were coarser compared to the nugget zone. A W-shaped microhardness profile appeared across layer interfaces. These findings contribute significantly to advancing the FSAM technique, particularly in manufacturing multi-layered, multi-pass laminates.
Keywords: Friction stir additive manufacturing (FSAM), surface hardness, microstructure evolution, grain refinement, AA 7075-T651
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Influence of processing and post-processing on microstructure and mechanical properties
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |